cinnamaldehyde
Synonyms: "cinnamic aldehyde", "3-phenylacrylaldehyde", "Cinnamal", "(E)-cinnamaldehyde", "3-phenylpropenal", "zimtaldehyde", "phenylacrolein", "cinnamylaldehyde", "(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enal", "cassia aldehyde", "trans-Cinnamic aldehyde", "(E)-3-Phenylpropenal", "3-Phenylacrolein", "(E)-3-Phenyl-2-propenal", "Cinnemaldehyde", "(E)-3-phenylprop-2-enal", "cinnamyl aldehyde", "3-phenyl-2-propenal", "benzylideneacetaldehyde", "beta-Phenylcrolein".
Source: Cinnamaldehyde is used in foods, beverages, medical products, perfumes, cosmetics, soaps, detergents, creams, and lotions. Cinnamaldehyde has been used as a filtering agent and a rubber reinforcing agent and is used as a brightener in electroplating processes, as an animal repellent, as an insect attractant, and as an antifungal agent.
Identifiers:
IUPAC Name: (E)-3-phenylprop-2-enal
CAS Number: 104-55-2
PubChem ID: 637511
InChiKey: KJPRLNWUNMBNBZ-QPJJXVBHSA-N
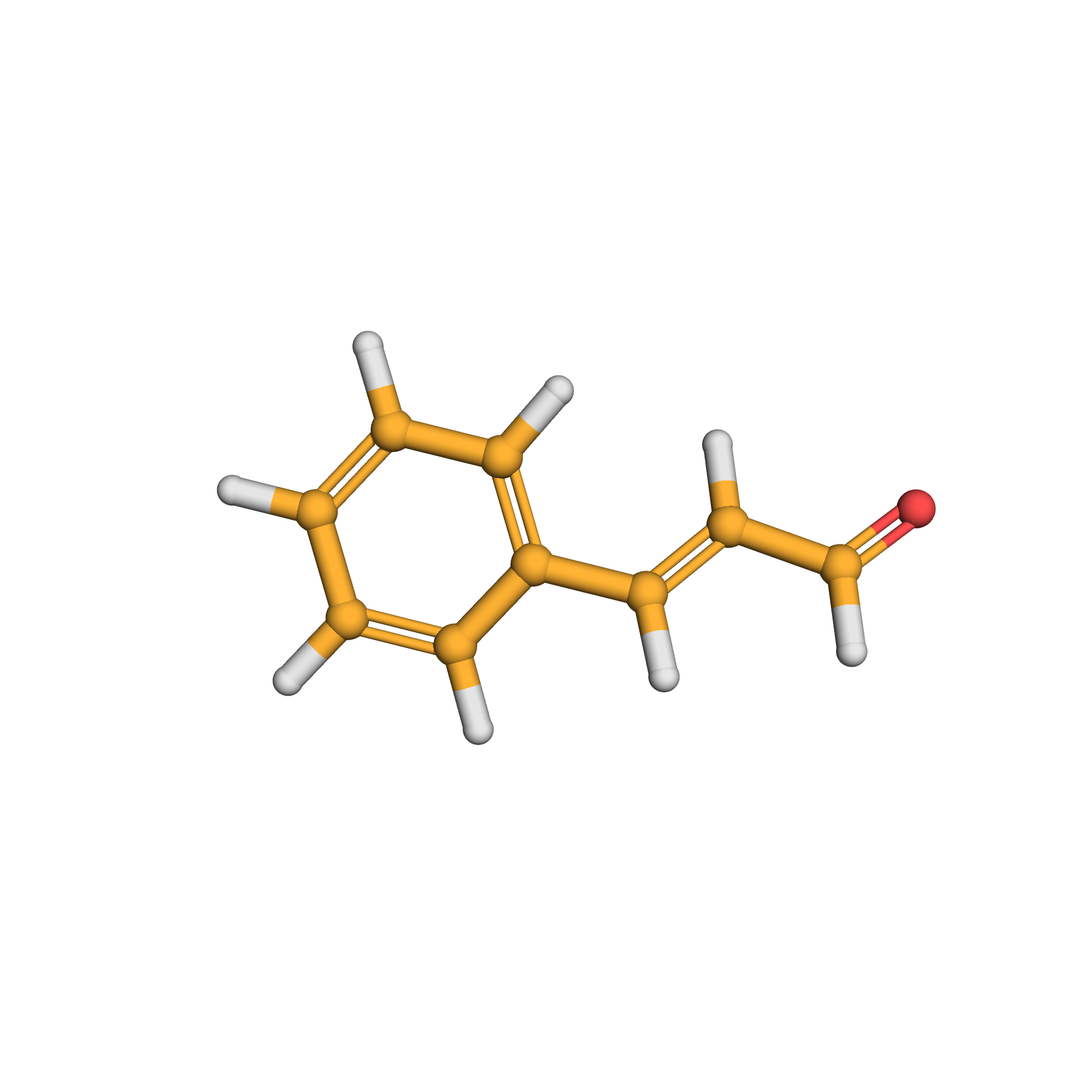
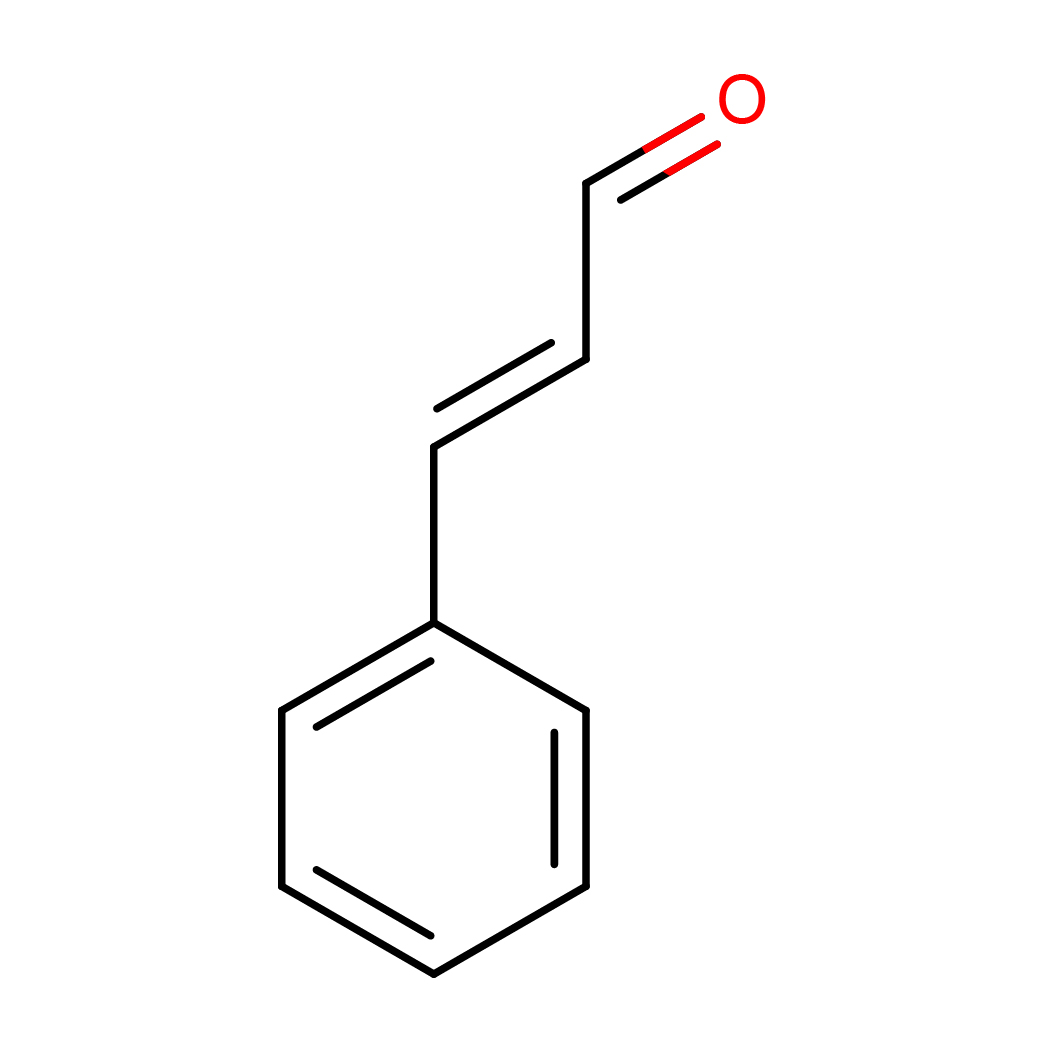
Canonical SMILES: C1=CC=C(C=C1)C=CC=O
Structural Properties:
Molecular Formula: C9H8O
Molecular Weight: 132.162
Pharmacophore Features:
Number of bond donors: 0
Number of bond acceptors: 1
Number of atoms different from hydrogen: 10
Downloads
2D structure (.sdf)
3D structure (.sdf)
3D structure (.mol2)
3D structure (.pdb)
3D structure (.pdbqt)
Search Similar molecules
Evidence Supporting This Chemical as an Endocrine Disruptor
TEDX List of Potential Endocrine Disruptors

Hebert CD, Yuan J, Dieter MP. 1994. Comparison of the toxicity of cinnamaldehyde when administered by microencapsulation in feed or by corn oil gavage. Food Chem Toxicol 32(12):1107-1115. DOI: 10.1016/0278-6915(94)90126-0. URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0278691594901260.
Mantovani A, Stazi AV, Macri C, Ricciardi C, Piccioni A, Badellino E. 1989. Pre-natal (segment II) toxicity study of cinnamic aldehyde in the Sprague-Dawley rat. Food Chem Toxicol 27(12):781-786. DOI: 10.1016/0278-6915(89)90108-7. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0278691589901087.
External Links





2D-structure
3D-structure