parathion
Synonyms: "ethyl parathion", "alkron", "paraphos", "thiophos", "corothion", "corthione", "danthion", "fosfive", "fosova", "diethyl p-nitrophenyl thiophosphate"
Source: parathion is a potent insecticide and acaricide.
Identifiers:
IUPAC Name: diethoxy-(4-nitrophenoxy)-sulfanylidene-?5-phosphane
CAS Number: 56-38-2
PubChem ID: 991
InChiKey: LCCNCVORNKJIRZ-UHFFFAOYSA
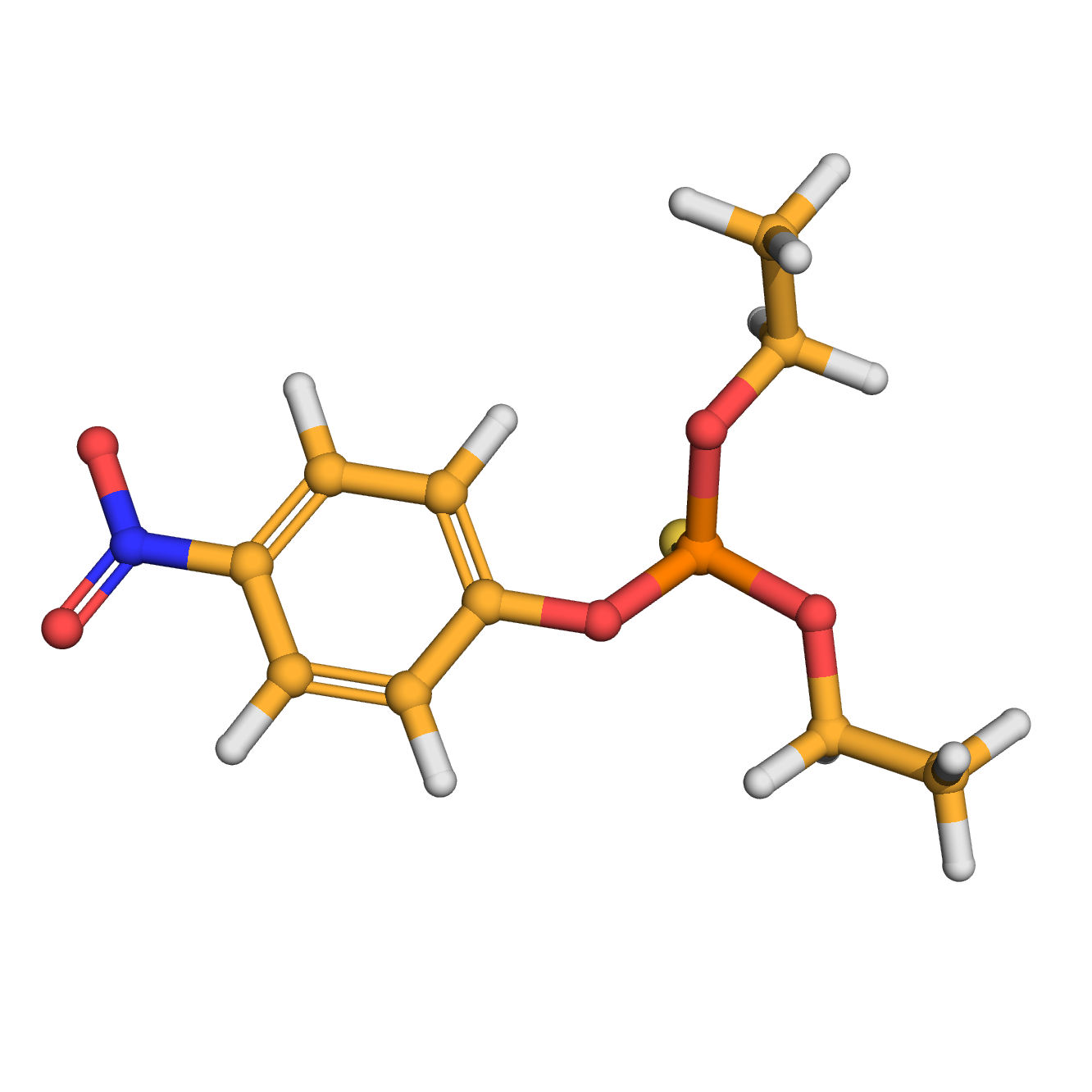
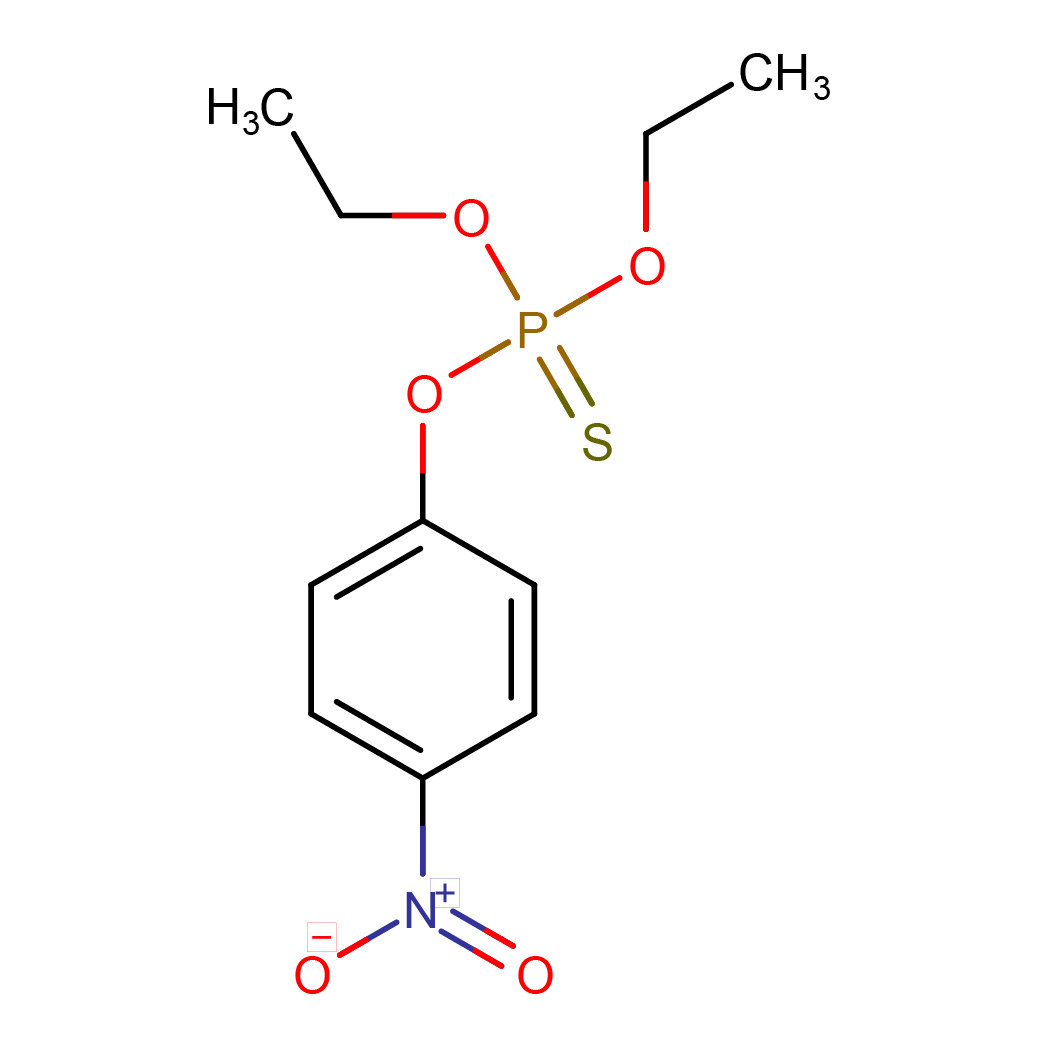
Canonical SMILES: CCOP(=S)(OCC)OC1=CC=C(C=C1)[N+](=O)[O-]
Structural Properties:
Molecular Formula: C10H14NO5PS
Molecular Weight: 291.261
Pharmacophore Features:
Number of bond donors: 0
Number of bond acceptors: 2
Number of atoms different from hydrogen: 18
Downloads
2D structure (.sdf)
3D structure (.sdf)
3D structure (.mol2)
3D structure (.pdb)
3D structure (.pdbqt)
Search Similar molecules
Evidence Supporting This Chemical as an Endocrine Disruptor
TEDX List of Potential Endocrine Disruptors

Klotz DM, Arnold SF, McLachlan JA. 1997. Inhibition of 17 beta-estradiol and progesterone activity in human breast and endometrial cancer cells by carbamate insecticides. Life Sci 60(17):1467-1475.
Kojima H, Katsura E, Takeuchi S, Niiyama K, Kobayashi K. 2004. Screening for estrogen and androgen receptor activities in 200 pesticides by in vitro reporter gene assays using Chinese hamster ovary cells. Environ Health Perspect 112(5):524-531.
Rattner BA, Clarke RN, Ottinger MA. 1986. Depression of plasma luteinizinag hormone concentration in quail by the anticholinesterase insecticide parathion. Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology C 83(2):451-453.
van den Berg KJ, van Raaij JAGM, Bragt PC, Notten WRF. 1991. Interactions of halogenated industrial chemicals with transthyretin and effects on thyroid hormone levels in vivo. Arch Toxicol 65(1):15-19.
External Links


2D-structure
3D-structure