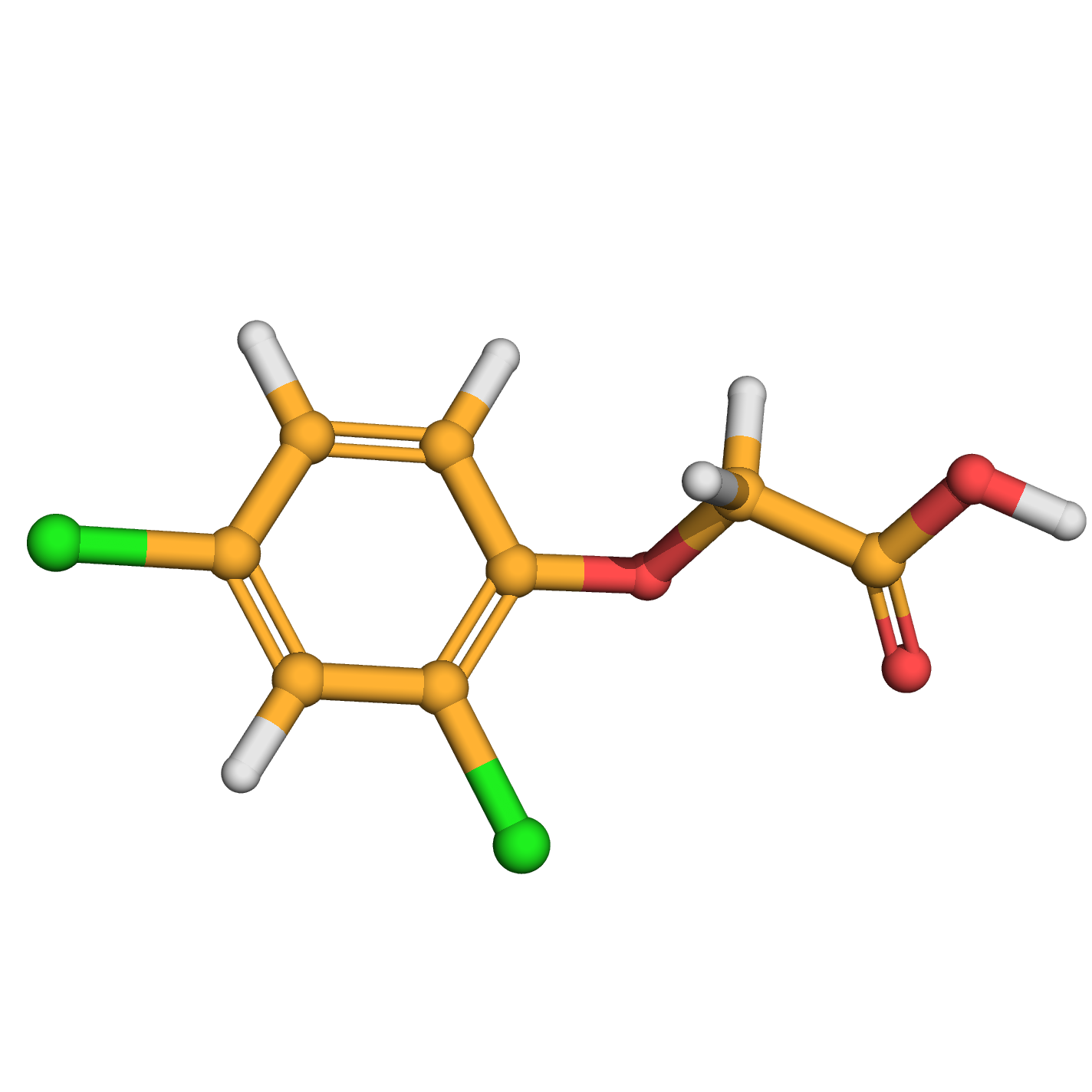
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
Synonyms: "hedonal", "(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid", "agrotect", "fernesta", "fernimine", "netagrone", "tributon,"2,4-D"
Source: 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is a systemic herbicide used post emergence for the control of broadleaf and grass weeds on crops, commercial and industrial areas, turf, forestry and waterways.
Identifiers:
IUPAC Name: 2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid
CAS Number: 94-75-7
PubChem ID: 1486
InChiKey: OVSKIKFHRZPJSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Canonical SMILES: C1=CC(=C(C=C1Cl)Cl)OCC(=O)O
Structural Properties:
Molecular Formula: C8H6Cl2O3
Molecular Weight: 221.037
Pharmacophore Features:
Number of bond donors: 1
Number of bond acceptors: 3
Number of atoms different from hydrogen: 13
Downloads
2D structure (.sdf)
3D structure (.sdf)
3D structure (.mol2)
3D structure (.pdb)
3D structure (.pdbqt)
Search Similar molecules
Evidence Supporting This Chemical as an Endocrine Disruptor
TEDX List of Potential Endocrine Disruptors

Cheney MA, Fiorillo R, Criddle RS. 1997. Herbicide and estrogen effects on the metabolic activity of Elliptio complanata measured by calorespirometry. Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 118(2):159-164.
Florsheim WH, Velcoff SM. 1962. Some effects of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on thyroid function in the rat: Effects on iodine accumulation. Endocrinology 71(1):1-6.
Kanayama T, Kobayashi N, Mamiya S, Nakanishi T, Nishikawa J. 2005. Organotin compounds promote adipocyte differentiation as agonists of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor [gamma]/retinoid X receptor pathway. Mol Pharmacol 67(3):766-774.
Van den Berg KJ, van Raaij JAGM, Bragt PC, Notten WRF. 1991. Interactions of halogenated industrial chemicals with transthyretin and effects on thyroid hormone levels in vivo. Arch Toxicol 65(1):15-19.
External Links


2D-structure
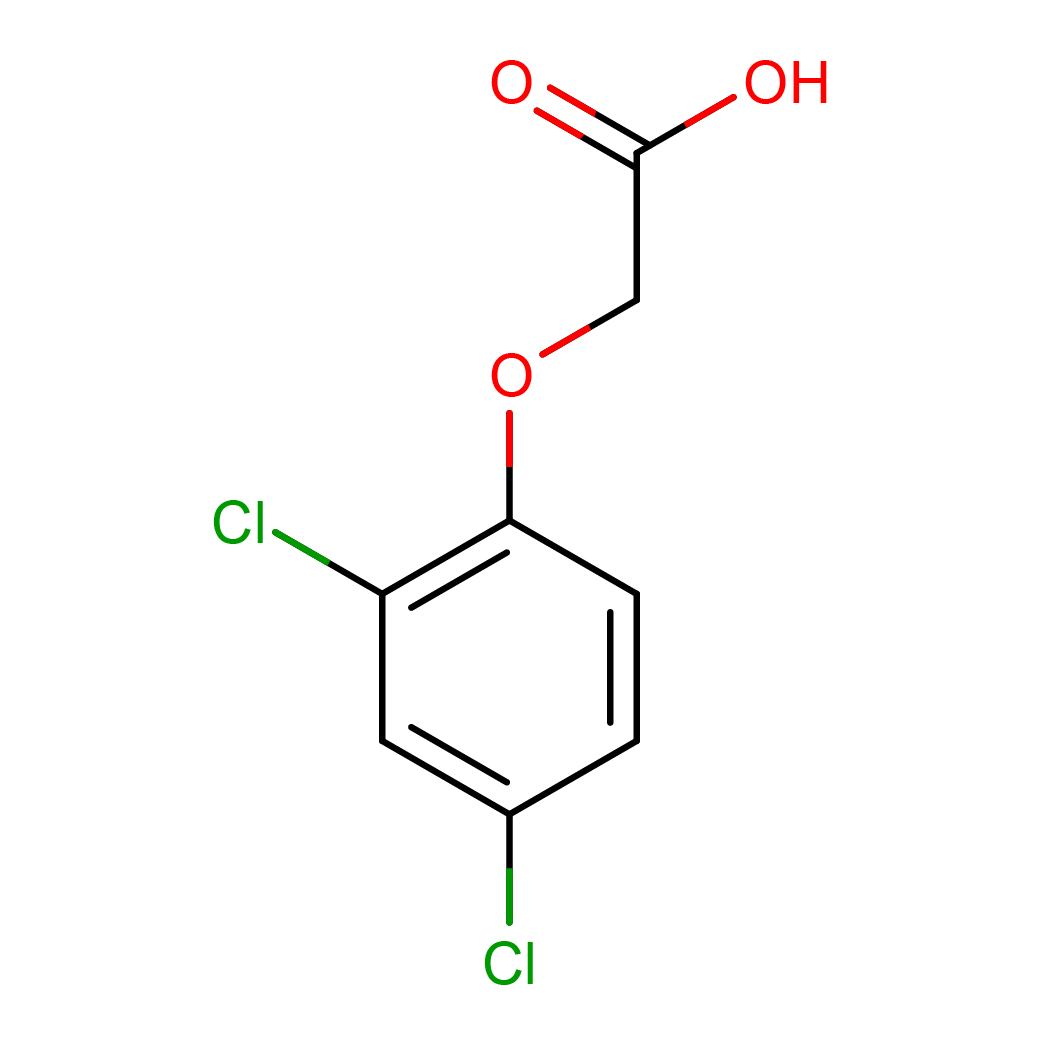
3D-structure